Intimate Partner Violence: A Community Response Model
At your last doctor’s visit, did anyone ask if you were safe at home? It’s important to know why you are being asked about your intimate relationships and what happens if you say that you are not safe.
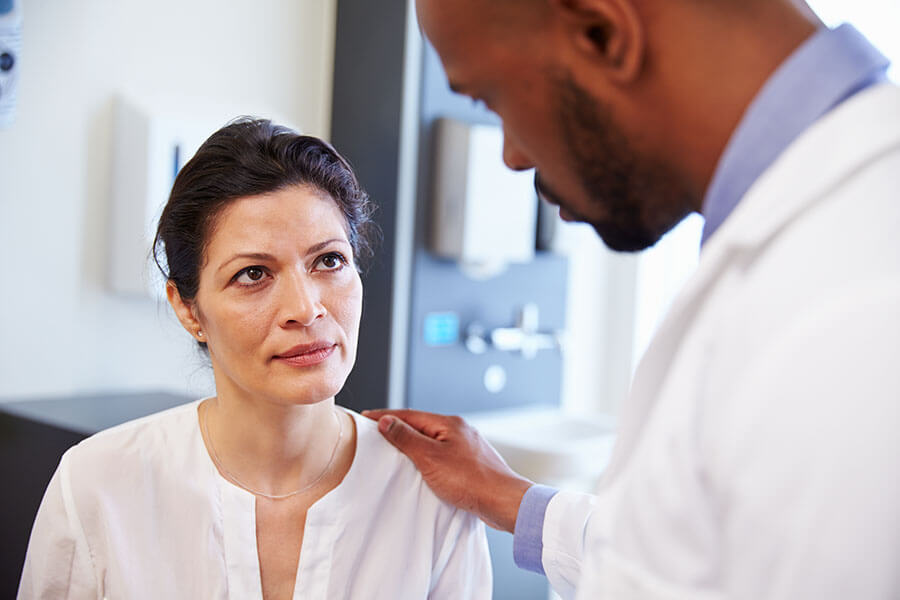 Approximately 1 in 3 women in the United States report experiencing some form of intimate partner violence (IPV) in their lifetime. Symptoms such as chronic migraines, insomnia, gastrointestinal issues, anxiety, depression, and numerous other health effects are experienced by survivors. Not having a safe person to talk with or a safe place to talk about IPV can prevent someone from getting help. Often, survivors feel a sense of security around medical professionals, which makes them more likely to disclose IPV in a health care setting. The M Health Community Network project (a grant funded by the Office on Women’s Health) is facilitating care for survivors with the use of a coordinated clinic and community response model that is supported by a partnership among researchers, the Domestic Abuse Project (DAP, a nonprofit based in Minneapolis, Minnesota), and the University of Minnesota’s Clinics and Surgery Center (CSC). Through the project, the Domestic Abuse Project brought on a full-time case manager to support referrals from the CSC and develop new partnerships in the community. As part of the project, rooming staff at the CSC were trained to screen all adult patients for IPV. If a patient indicates past or present partner violence, they have the opportunity to be connected with a member of the clinic’s Behavioral Health Team (BHT) who can meet during that same visit and provide immediate support, mental health referrals, and safety planning.
Approximately 1 in 3 women in the United States report experiencing some form of intimate partner violence (IPV) in their lifetime. Symptoms such as chronic migraines, insomnia, gastrointestinal issues, anxiety, depression, and numerous other health effects are experienced by survivors. Not having a safe person to talk with or a safe place to talk about IPV can prevent someone from getting help. Often, survivors feel a sense of security around medical professionals, which makes them more likely to disclose IPV in a health care setting. The M Health Community Network project (a grant funded by the Office on Women’s Health) is facilitating care for survivors with the use of a coordinated clinic and community response model that is supported by a partnership among researchers, the Domestic Abuse Project (DAP, a nonprofit based in Minneapolis, Minnesota), and the University of Minnesota’s Clinics and Surgery Center (CSC). Through the project, the Domestic Abuse Project brought on a full-time case manager to support referrals from the CSC and develop new partnerships in the community. As part of the project, rooming staff at the CSC were trained to screen all adult patients for IPV. If a patient indicates past or present partner violence, they have the opportunity to be connected with a member of the clinic’s Behavioral Health Team (BHT) who can meet during that same visit and provide immediate support, mental health referrals, and safety planning.
One of the most significant relationships fostered through the project has been between the BHT and the DAP case manager. This relationship is important in serving women who experience IPV, especially since each woman’s situation is unique. Survivors’ needs vary and may include assistance accessing basic services, obtaining legal and financial support, and accessing mental and behavioral health care. Patient needs are assessed and supports are individually tailored, ensuring a warm hand-off to community services. In this client-centered model, patients have reported feeling heard, believed, and supported.
One example is the story of Sarah, who was screened for IPV at one of the clinics and referred to the DAP by the BHT. Sarah told the DAP case manager that she had never been more afraid or ashamed in her life. After 10 years of keeping a family secret, she shared her experiences and felt like a load had been lifted. She said she thought something like this could never happen to her or her family. She was connected to group therapy and became more emotionally stable as the weeks went by.
We all can take part in ending IPV. We can start by listening: If someone confides in you, listen without judgment. All too often survivors will open up and talk about their own abuse, only to be discouraged by an unsupportive response. Even when survivors are ready to seek help, knowing where to start can be a challenge — survivors may be unaware of community resources, care, and other forms of support available to them. As October is Domestic Violence Awareness Month, now is a perfect time to reflect on the range of community health care linkages that can bridge the gap in awareness and services that many survivors face. Safety is the responsibility of all of us. Help break the cycle of violence by bringing domestic violence and IPV awareness to your community.
The Domestic Abuse Project (DAP) is a community agency that has provided individual and group therapy to Minneapolis-area families since 1979. DAP’s mission is to build communities free from violence by providing holistic healing for every member of the family.
If you or someone you love is being abused, help is available. Call the National Domestic Violence Hotline at 1-800-799-7233 or 800-787-3224 (TTY).